Distribution
![]() News
News
![]() Notes & Interesting Articles
Notes & Interesting Articles
![]() Overview
Overview
![]() Pricing
Pricing
![]() Products
Products
Accessories and Options
![]() Filters
Filters
![]()

Baader Planetarium UHC-S (Ultra High Contrast) Nebula Filter
Right: Baader 2 and 1.25 inch UHC-S filters. When viewed parallel to the eye then the filter element appears like a silvered mirror. (136,193 bytes).
The UHC-S performs a function somewhere between that of the very narrow bandpass Baader Oxygen III, and others that are broad bandpass filters. This Nebula Filter is recommended by Company Seven to our customers who have a suitable telescopes: including premium quality Apo refractors of 80mm and larger aperture, Achromatic refractors of 100mm and larger, or reflectors of 8 inch (20cm) or larger).
How Do Nebula filters Work?
Street lights, especially the poorly baffled ones, cast a greenish or golden glow upon the otherwise black night sky. Particulates and humidity in the atmosphere refract and reflect that light rendering the sky background brighter, hence the fainter objects become harder to see against the brighter background. Nebular filters filter out a high percentage of the street lighting effects thereby making the background of the night sky appear blacker; faint objects stand out better against the darker background. While these are obviously beneficial for those who live near sky light polluted suburban areas, Nebular filters are helpful even when observing at darker rural settings since they also filter some of the naturally occurring background glow. Note, these filters can not help to attenuate light from neon sources since these emit across a wide bandwidth.
Narrower, and narrower bandpass filters become more and more specialized and may actually cut down the light coming from some of the brighter emission nebula; for example M42 the Great Nebula in Orion looks great with no filter, better with a broad band nebula filter, but much of the extended portions of the nebula disappear when observed with a very narrow band filter.
In the way these filters work, they will still absorb some light from desired object. And there are objects that they can not help one to see better including stars, star clusters and galaxies since these emit light from all wavelengths including those emitted by street lights. And so a pronounced darkening of these objects will be observed with the filter in place.
Observers with smaller telescopes will do best to operate at the lower magnifications, on the order of 10x or less per inch of aperture. While those with larger apertures or more efficient mid to large refractors will do well to span from low to higher magnifications.
Nebular filter coatings present a metallic, mirror like quality. As such one should use care to use the filters away from bright sources of stray light an with a well baffled telescopes. A darkening hood or blanket over the observer's head may help to keep reflections coming back to the observer, and darken the sky background seen even further.
How Are These Constructed?
The filter is then housed in a machined aluminum cell by a thread in retaining ring. The filter name, size and part number are in silver, and this mirror like print when combined with the fine print make this information difficult to read under dim red lighting. Company Seven recommends our customers keep these filters in well organized accessory cases, so that you know which filter is which. It helps to become familiar with how the elements appear too (read descriptions below).
Nebula Filters are made up of micron thin layers of materials deposited onto an otherwise transparent optical glass window. The coatings are calculated to transmit desired wavelengths (portions of the visible spectrum), while simultaneously rejecting a high percentage of other wavelengths. Depending on the type of filter (broad band pass or narrow band filters including UHC-S) these filters pass light in the nebula lines which may include UHC-S, Hydrogen Alpha, and Hydrogen Beta lines of the spectrum. In a more perfected nebula filter a higher percentage of light is transmitted in those desired wavelengths, as much as 80 to 90 percent being typical.
When tilted while exposed to bright light then both surfaces of the UHC-S filter element will appear like a silvered mirror. When viewed with no backlighting and parallel to the eye from either side, then the filter element appears to impart a light green cast. When tilted with respect to the observer's position this light green changes to magenta gradually becoming deeper in color, as the tilt increases even farther then the intense magenta cast diminishes to a light pink.
The Baader UHC-S filter is made available in diameters of 1.25 (31.7 mm) or 2 inch (50.8 mm) so that it can be installed in line onto many accessories, or directly onto most popular eyepieces.
What Does This Do For Me?
It is an amazing experience to see a faint planetary nebula clearly revealed in the field of view - obvious even to a child,
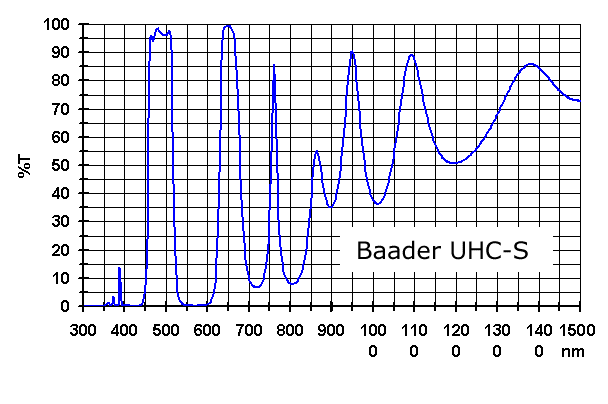
Right: Baader UHC-S filter transmission curves. (145,382 bytes).
Features Of The Baader Filters:
Examples of Imaging with the UHC-S Filter:
Above (Left to Right): M8 Lagoon Nebula, 2x 10 minute exposures. Helix Nebula
2x 10 minute exp.
Above: Bug Nebula, 2x 10 minute exposures. IC 4628 im Skorpion
2x 10 minute exp. M8 Lagoon Nebula taken during full moon.
The optional wood case is foam lined with cutaway spaces for filters, eyepieces and other small accessories for your telescope. Please refer to our price list for current prices for the filter set and the optional case or contact Company Seven for more information.
Right: optional wood box for Color Filter Set (52,803 bytes)

Filters take away but they can not add - diminishing some parts of the spectrum
so that we might see what is otherwise obscured...
These filters are a helpful accessory used with telescopes and binoculars to better view or photograph some types of the faint objects outside the Solar System. Filters of the UHC-S variety specialize in showing diffuse emission and planetary nebula; they are not designed to improve the views of objects outside these categories.
The filter is made with a disc of transparent optical glass that has been ground to be plane parallel and then polished until very smooth. The glass undergoes a vacuum deposition coating process where numerous micron-thin coatings of various elements are applied one upon another in a precise order and thicknesses.
This filter is among the better mid transmission nebula filters on the market as such it effectively blocks the entire visual spectrum with the exception of the O-III transmission lines. By means of its sophisticated optical fabrication and coating technologies it eliminates the annoying colored halos that often surround stars when seen though some other O-III filters. It is a surprisingly long lived, durable filter featuring the same ultra-hard, extremely durable vacuum-deposited dielectric coatings employed on the Baader UHC-S-S filter.
when before then there was not even the slightest suggestion of its presence without the UHC-S filter in place



Trifid Nebula 1x 10 min and 1x15 minute exp. combined.
All images by 10 inch f/5.6 reflecting telescope (note diffraction spikes), Canon 300d camera with ISO 1600 film.
Copyright Mr. Scott Alder, N.S.W. Australia.
Click on images to see enlarged view
Optional Wood Case
Click on the image to see enlarged view (190,049 bytes).
FURTHER READING
CLEANING & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS:
![]() Baader Planetarium Professional Astronomical Filters one page color illustrated overview of several Baader specialized astronomical filters including the UHC-S Narrow Band, Contrast Booster, Color Filter Set, UV-IR Rejection, Fringer Killer, Moon and SkyGlow, Solar Continuum, UHC-S-S High Transmission Nebular. Includes filter transmission curve graphs. Publication content by Baader Planetarium, all rights reserved. From Company Seven's Archives (127,011 bytes in Adobe .pdf).
Baader Planetarium Professional Astronomical Filters one page color illustrated overview of several Baader specialized astronomical filters including the UHC-S Narrow Band, Contrast Booster, Color Filter Set, UV-IR Rejection, Fringer Killer, Moon and SkyGlow, Solar Continuum, UHC-S-S High Transmission Nebular. Includes filter transmission curve graphs. Publication content by Baader Planetarium, all rights reserved. From Company Seven's Archives (127,011 bytes in Adobe .pdf).
Contents Copyright 1999-2006 Company Seven All Rights Reserved